How Much Physical Security is Enough?
When it comes to security, physical security is something which either takes a back seat or is not dealt with expertise. Though there are a lot of solutions present in the market for physical security, but choosing the right option is a task. A detailed analysis is required to determine the correct controls, correct implementation, and cost. Each organisation has its own set of test cases, priorities, budget, and expectations from the products available. Since the solutions are not a one size fits all, each solution comes with its own bag of prerequisites, limitations, and troubleshooting or handling overheads. In this article, I will be discussing physical security control which should be in place for a typical corporate office. Although all controls are not required for every office, what to choose and what not should be analysed and decided.
Corporate office scenario


FREE role-guided training plans
- Amber: It depicts the campus of the company. It will house the parking, safe assembly areas, cafeteria, etc.
- Blue: it is the corporate office itself where the employees will be present for most of the time. There can be multiple offices in the same campus for the same company or different companies.
Choosing a secure physical location for the campus/building
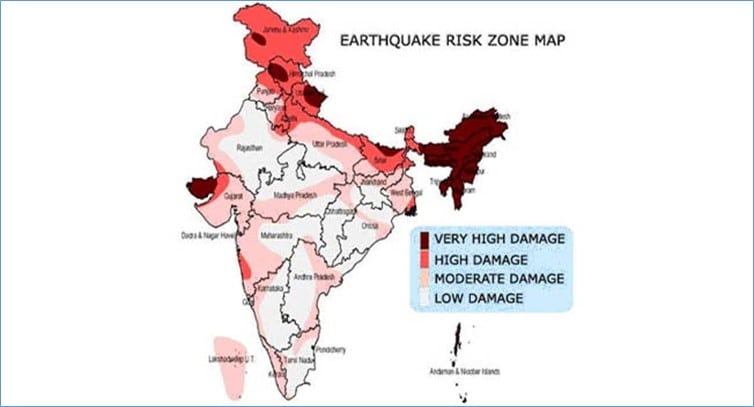
Climate and disasters: Organisations must consider the location of the building and should take time in accessing the climate and disasters which the area is prone to. This is something which will be most expensive to change once the services are up. A few questions for the organisations to ponder on – Is the climate suitable? It will affect both the office building and the employees. Is the office present in earthquake prone zone? – Is yes, then which category (1, 2, 3, 4), this will help the organisation to decide if they are ready to go ahead as they will require additional controls in place to protect the building and staff.
Location considerations: Is the location suitable? In what type of area does the office lie? – Industrial area, residential area, city outskirts, etc. If it lies in a residential area then getting a place there will be a challenge for the organisation, there will be other legal implications which the organisation has to deal with. If the area is an industrial area there will be noise pollution, vibrations, air pollution have to be kept in mind. Getting to know the crime rate of the area will help the organisation to ensure the safety of the employees.
Accessibility and services: To check for nearby traffic patterns, power outage patterns, proximity to fuel pumps, medical services and fire station and police facilities should be on the plan as well. You do not want your employees to be late by getting stuck in the local traffic. Getting all services arm's length will be a dream but too far from these services will also be a matter of concern.
Physical Security designing and access controls
Exterior walls: Strong exterior walls can be an option if you want to protect the office from hurricanes. Having strong exterior walls is a necessary for the campus but for a building inside campus this might not be the best option. Shatter proof glass with metal bar support will do the job as this will not cut the overall visibility and will also provide external security.
Control placement: External walls for the corporate office and campus
Interior walls: Should internal walls be the same as internal walls? Internal walls can be made of concrete, Ply, bullet proof Kevlar, etc. If the area houses a critical server of an asset then making a plywood wall boundary around it will not be the best option. The point to consider here is that what purpose the wall is required for. Is it protecting an asset or just to create a segment? The material and strength can be decided further.
Control placement: All walls inside the corporate office
Doors: Doors must be strong to resist forcible entry. Doors must be monitored and alarmed (long open timer) for unauthorized entry. There must be clear warnings on the doors like "No tailgating" and "emergency exit." The location of handles is also a matter of concern; emergency exits must have handles only inside and no locks, latches from the outside. You do not want your employees to be locked from outside in case of a fire. The doors should be fail-safe so that even in the event of an emergency the safety of the employees is not compromised.
Control placement: All entry and exit points inside and outside the corporate office.
Lighting: The lighting should be adequate thus making sure that there are no blind spots in the area. The options for lighting can be strong high beam for perimeter security and led options for internal lighting. There should be adequate lighting over the workstations.
Control placement: All places including parking, lobby, and campus. All places should be well lit.
Heat ventilation and Air Conditioning: There should be adequate planning for HVAC systems. The moisture content must also be monitored and controlled. Moisture can damage the equipment and low.
Control placement: Corporate office
Pipes and Drains: The plan for drains and pipes must be analysed carefully. There should be adequate markings on the pipes and valves. The drainage should have a positive flow away from the building and should not get blocked or back flow in case of heavy rains.
Control placement: Campus and corporate office, includes fire water pipes, sewage drains, water pipes, etc.
Fencing: Fencing is required in the external perimeter of the building. This will provide a deterrent control as well as protection from trespassers. The height should not be so less so that anyone can climb and not too high so that it becomes difficult for the maintenance personnel.
The cost plays an important role when fencing is concerned.
Control placement: Around the campus and/or around the corporate office if required.
Mantraps: As the name suggests, traps the man inside a double set of locked doors. The trap can have multiple exits based on the access types. A more advanced version of the mantrap can have a weight sensor; this makes sure that only one person enters the mantrap at one time.
Control placement: Entry to the corporate office. Placement at emergency exits will not be a good option.

Guards and dogs: Guards can provide physical security for different environments. In spite of all the surveillance equipment and modern technology a skilled guard is required to monitor these controls and take appropriate action. There are various advantages of having a guard. He can apply human judgement to the conditions, provide a physical deterrent and perform various other jobs. The dark side is that there can be human errors and significant cost. Dogs can also be used as a deterrent control, but they have to be maintained and have other liability issues associated with them.
Control placement: Campus entry and exits, corporate office entry and exits, parking entry and exits.
Boom barriers and vehicle entry: For any vehicle entering or exiting the building there has to be a security check post which allows tracking and authorizing vehicle entry and exits. There should be sample check of reconciliation between the vehicles entering and exiting the facility.
Control placement: Parking entry and exits.

Security badges for auto mobiles and employees: Authorized vehicles and guest vehicles should have a separate parking space, and they must be provided with visible badges which should be unique and difficult to forge. Employees should be provided with a photo id card so that they can be easily identified. Visitors should be provided with a separate kind of identity card so that they can be identified explicitly. Smart cards can be provided or integrated with the ID card so as to provide access to the relevant area. There are many types of card when it comes to access control – Magnetic strip, optical encoded, Chip cards. Biometric controls can also be placed to allow aces to a particular area, but the cost factor can be a tie breaker between smart cards and biometric controls.
Control placement: Employees, visitors, and vehicles.

Locks: Locks can be either mounted over the door, inside the hinge. These provide a mechanism of physically bolting the door along with automated access controls.
Control placement: All doors, emergency doors should have locks only from inside and not outside.
Technical controls
Surveillance: CCTV s can provide a way for the security personnel to do surveillance. CCTV s can be installed and monitored. The location of the CCTV is important as we need to make sure that there is no blind spot and all entry exits are covered. The recordings can be used to identify the culprit and serve as evidence in case if any incident or security breach. The positioning of the CCTVs should be such that they cannot be easily reached or damaged. Since they become our eyes and ears, they need to be secured properly.
Control placement: Campus area, corporate office. Can be mandatory at entry and exits.
Intrusion detection: Motion sensors, light sensors, heat sensors can be placed at a location which requires extra protection. There can be no point placing a motion detector in the cafeteria but in server room motion sensor can serve a purpose where you do not expect someone to be present every time.
Control placement: As per need. Server room, archive room, etc.
Alarms: These can be used so as to inform the correct person about any potential incident so that that appropriate action can be taken. The alarm can be placed near the sensor itself, or at a central monitoring room, remote location or at the nearby policy or fire station if required. Alarms just serve as a detection mechanism, and appropriate actions must be decided in the event an alarm goes off. There should be adequate safety for the alarm so that an attacker does not disable the alarm itself.
Control placement: Entry and exit doors. Corporate office and campus in case of fire.

Environmental and life safety controls
Electric power: Power sources would be clean and reliable. There should be some arrangement of secondary power as well. DG, UPS, or natural gas can be used but natural gas cannot be stored locally, and there can be leakage as well. The UPS can provide instantaneous power until the time DG kicks in. UPS cannot be used as the only back up as it will not last in case of long power cuts. The DG has to be tested with a full load and operational load. An adequate supply of fuel should be maintained along with the appropriate process to get more fuel of required. The power switch should be maintained near an emergency exit door so that the electricity can be shut off in the case of a fire of other disaster.
Fire detection and suppression: To detect fire, an appropriate sensor needs to be in place. Below are the types of sensors which can be installed.
- Heat sensing (detects temperature changes)
- Flame sensing (Detects flame pulses)
- Smoke sensing (Analyses smoke)
Suppression systems are required to control/extinguish the fire and are mainly of two types:

FREE role-guided training plans
-
Water
- Wet pipe (water will already be filled)
- Dry pipe (Water will enter post valve is opened – delayed action)
- Deluge (Dry pipe but delivers large volume of water quickly)
-
Gas
- Co2
- Soda acid
- Gas discharge (Use of inert gases)
A fire alarm switch has to be placed at appropriate places, so that fire signal is propagated effectively. There should be fire drills performed at regular intervals so that employees are well aware how and what to do in case fire alarm goes off. There should be segregation of duties as well such as fire warden at each floor or multiple at a floor which can coordinate and ensure the safety of the employees at the time of need. A medical safety person should be assigned to provide medical assistance to the injured persons. Fire warden and first aider should be well trained, and there should not be a single point of failure, multiple persons can be assigned the job.




