Cyber-espionage: The greatest transfer of wealth in history
Introduction
In recent months, the world-wide security community has discovered many cyber espionage campaigns that hit governments, intelligence agencies and private industry. The majority of them were related to state-sponsored hackers, while others were organized by groups of cyber criminals having obtaining access in order to resell sensitive information and intellectual property.
There is no specific area of the globe subject to the majority of cyber espionage attacks. Typically, they center on the most technologically advanced countries: the US, Japan and Russia, mostly. But a good number of operations have also been detected in problematic regions like the Middle East as well.
The technologies used to spy on victims, and the motivations behind them vary. Network surveillance appliances, communication cracking techniques, malware and "social network poisoning" are just a few of the methods adopted for political, economic or criminal intents. Profit, power and protest are the main motivations behind the attacks, radically affecting a user's approach to the web and its perception of security.
Cybercrime, governments, and groups of hacktivists tend to lean toward the spread of malicious agents that have the capacity to silently infiltrate their targets, stealing confidential information from them. The Chinese government is considered the biggest aggressor in cyber espionage, while US networks are the privileged targets of cyber attacks that hit every sector, from media to military.
A report published in 2012 by the U.S. China Economic and Security Review Commission revealed that "U.S. industry and a range of government and military targets face repeated exploitation attempts by Chinese hackers, as do international organizations and nongovernmental groups including Chinese dissident groups, activists, religious organizations, rights groups, and media institutions."
"In 2012, Chinese state-sponsored actors continued to exploit U.S. government, military, industrial, and nongovernmental computer systems,"
The report revealed that Chinese cyber exploitation capabilities last year were "improving significantly." But while the US has as many enemies as allies, all of us in the cyber era are potential victims. The number of state-sponsored attacks is increasing in impressive ways, due to the commitment of governments to cyber technology.
According to the last report of F-Secure related to H2 2012, one of the most interesting phenomena observed in the period is the changing of techniques for cyber espionage campaigns. To this point, almost all recorded corporate espionage cases were based on using specially-crafted documents containing a malware payload; meanwhile, in Q4, the attackers have started to exploit vulnerabilities in in web browsers and browser plugins.
The consolidated technique known as the 'watering hole' attack was the most efficient for cyber spies, capable of infecting every visitor of a particular website compromised for the campaign.
"The rise of web-based attacks in corporate espionage raises two points: first, this trend means that any corporation with an online presence that serves such potentially 'interesting' targets may be at risk of unwittingly serving as an attack conduit, and secondly; obviously, such organizations must now find a way to mitigate such a risk, in order to protect themselves and their clients."
[caption id="" align="alignnone" width="569"]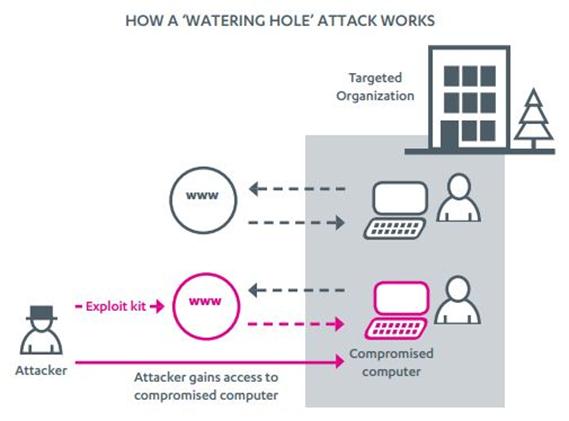 Figure 1 - Waterering Hole attacks (F-Secure)[/caption]
Figure 1 - Waterering Hole attacks (F-Secure)[/caption]
Every company that manages online resources must be aware of this technique of attack. Defending against watering hole attacks does not require additional defense systems, save for attacks that exploit zero-day vulnerabilities against which a multi layered security approach is necessary.
Cyber espionage Statistics
Estimating the real impact of cyber espionage on the global economy is quite impossible, due to the difficulty in identifying the majority of cyber attacks accounted for in each sector.
NSA Director General Keith Alexander called cyber-espionage "the greatest transfer of wealth in history." Symantec places the cost of intellectual property theft for U.S. economy at $250 billion a year, with cybercrime a further $114 billion annually. Meanwhile, McAfee provides an estimate encompassing global remediation costs to total a staggering $1 trillion per annum.
The UK Cabinet Office reports intellectual property theft and industrial espionage costs of £16.8 billion in 2012. The 2012 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) reported 855 security breach incidents in industrial and corporate networks, totaling 174 million compromised records across the US, UK, Holland, Ireland and Australia. Of these 855 incidents investigated by the DBIR, 92% went undiscovered until an external party revealed them.
The figures provided are very troubling. While enormous, we must remain conscious that the true extent of cyber-espionage is incalculable. Private companies and governments often do not report losses because in many cases, they aren't able to detect the attacks. When the cyber espionage campaigns are discovered, information on them may be kept secret for fear of brand and/or reputation damage, company devaluation and loss of public confidence.
In many cases, estimates provided on the impact of cyber espionage don't include the cost of defense systems deployed (and eluded by the cyber threats), as well as the cost of compensation and remediation actions of the victims.
Case Studies: Operations Aurora, The Elderwood project, Flame and Red October
If you ask a security expert to provide some examples of the most interesting cyber espionage campaigns in the history, you will probably hear about some of the following cases:
Operation Aurora was a cyber attack first publicly disclosed by Google on January 2010. It began in mid-2009 and continued through the end of the year. Google revealed that the sophisticated attacks originated in China, they were well-resourced and consistent with an advanced persistent threat attack.
The attacks were aimed at dozens of organizations operating in various sectors, including Adobe Systems, Juniper Networks, Yahoo, Symantec, Northrop Grumman, Morgan Stanley and Dow Chemical.
In September 2012, Symantec detected attacks that were part of a cyber espionage campaign called the "Elderwood Project." Their execution exploited various 0-day vulnerabilities in many large-use software including IExplorer and Adobe Flash Player. Symantec declared that some of the exploits had been realized from knowledge of a stolen source code, assuming a link with the known operation, Aurora. The attacks implemented "watering hole" techniques to infect the victims with malware, injecting malicious code onto the public web pages of sites that the targets visited.
The Flame campaign was discovered in May 2012 by Kaspersky Labs. The nature of the systems targeted and geographic distribution of the malware (the Middle East), combined with the high-level of sophistication led security experts to believe that it was developed by a foreign state, intent on hitting a specific country in the region. Flame is a complex malware, designed with the primary intent to create a comprehensive cyber espionage tool kit.
Most recently, the Red October campaign has been revealed by Kaspersky Lab's Global Research & Analysis Team. The investigation began after several attacks hit computer networks of various international diplomatic service agencies. This was a large-scale cyber espionage operation conducted to acquire sensible information from diplomatic, governmental and scientific research organizations in many countries; most of them in Eastern Europe, former USSR states and countries in Central Asia.
Unlike previous cyber espionage campaigns, Red October has targeted devices, including enterprise network equipment and mobile equipment (Windows Mobile, iPhone, Nokia). It hijacked files from removable disk drives, stole e-mail databases from local Outlook storage or remote POP/IMAP servers and siphoned files from local network FTP servers.
Most troubling was evidence collected that demonstrated the campaign began in 2007 and is still active. During the last 5 years, a huge quantity of data collected (including service credentials) has been reused in later attacks.
Reading the list of cases, one observes that many cyber espionage campaigns remained undetected for a long time. Resourceful attackers in fact used, in many cases, zero-day vulnerabilities that allowed them to elude detection by principal defense systems. In some instances, the hackers have stolen documents and sensitive information for years, changing the operative mode over time. This particularity led investigators to believe that the campaigns were organized and managed by groups of professionals possessing a variety of skills, including research capabilities to uncover and exploit unknown vulnerabilities.
On the Elderwood operation, Orla Cox, a senior manager at Symantec's security response division, reported that it has uncovered at least eight zero-day vulnerabilities since late 2010, and four since last spring. She said:
"We were amazed when Stuxnet used four zero-days, but this group has been able to discover eight zero-days. More, the fact that they have prepared [their attacks] and are ready to go as soon as they have a new zero-day, and the speed with which they use these zero-days, is something we've not seen before."
Symantec produced a detailed analysis of the phenomenon, stating:
"This group is focused on wholesale theft of intellectual property and clearly has the resources, in terms of manpower, funding, and technical skills, required to implement this task,"
"The group seemingly has an unlimited supply of zero-day vulnerabilities."
The level of sophistication of the attacks, the targets chosen and abilities shown by the attackers suggest the commitment of a foreign government. Moreover, security experts believe that in many cases, the campaigns are linked each other, citing the case of Operation Aurora and the Elderwood project. With a majority of attacks linked to state-sponsored actors capable of organizing so complex an operation, the investigation on Red October revealed the possible involvement of Russian RBN, long considered a cybercrime outfit capable of providing an array of malicious services, including phishing, DDoS, malware hosting, gambling and child pornography.
[caption id="" align="alignnone" width="509"]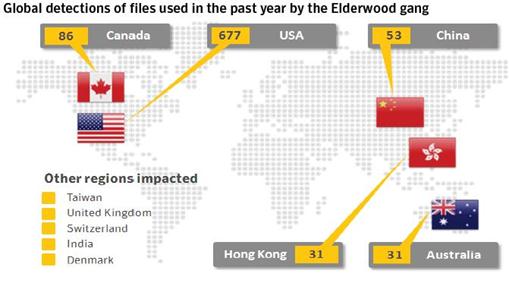 Figure 2 - Elderwood project global detections[/caption]
Figure 2 - Elderwood project global detections[/caption]
Cyber espionage and private businesses
Small business is the most vulnerable to cyber espionage. It represents an attractive target, due the lack of security mechanisms and processes as well as - in many cases - the direct relationship between enterprises and governments. In recent years, the number of attacks against government contractors has increased. A cyber attack against a subcontractor is easy to realize, as the line of defense penetrated is often fragile, allowing the attackers to acquire sensitive information from targets of interest.
Last year, Trend Micro reported an increase of focused attacks. Hundreds of millions threats were blocked from infecting small businesses, but large companies proved equally vulnerable, having been hit as part of the IXSHE campaign.
A recent study on cyber-espionage has demonstrated that more than 200 families of malware have been designed and used to spy on government and corporate representatives.We have assisted the diffusion of new agents that work in botnet architectures, as new variants - designed especially for mobile devices - are specifically developed for selected targets.
The primary intent of cyber espionage is to steal classified information from government agencies or trade secrets from corporations. This situation can be extremely dangerous for the economy of a company, as well as that of the overall country. As governments and businesses alike are motivated to reduce the technological gap with their competitors, it's clear how diffused the phenomenon is.
Cyber espionage can have a devastating effect on the social fabric of a nation as well as on the actions of every private company. It is sneaky and silent: unlike other crimes, it may be conducted for years without the victim being aware of it with serious consequences. This happened in the case of Nortel, a company which ended up in bankruptcy due to the theft of company secrets.
Last year, the Office of the National Counterintelligence Executive published a report to Congress, presenting a frightening picture of the degree to which other countries use cyber espionage to attempt to gain business and industrial secrets from US companies. The biggest cyber-espionage threats against American businesses come from China and Russia. These states engage in deliberate efforts to obtain sensitive business and technology information. The report concludes that China and Russia will "remain aggressive and capable collectors of sensitive US economic information and technologies, particularly in cyberspace."
"National boundaries will deter economic espionage less than ever as more business is conducted from wherever workers can access the Internet,""The globalization of the supply chain for new—and increasingly interconnected—IT products will offer more opportunities for malicious actors to compromise the integrity and security of
these devices."
The document called the Chinese government a "persistent collector": the most active one, while depicting Russia's intelligence services as conducting a range of activities to collect economic information and technology from US targets.
The increased number of malwares developed by governments to spy on their adversaries (such as Flame, Gauss and Duqu, as well as the recent "Operation Beebus" campaign) demonstrate the high interest of intelligence agencies to implement these methods to acquire restricted information.
Recently, MI5 issued 300 warning letters to UK business leaders highlighting the risk of "electronic espionage" from Chinese organizations. MI5 Director General Jonathan Evans declared that an "astonishing[ly]" high level of cyber-espionage campaign target Western countries on an almost industrial scale."
The number of corporate victims underscores a troubling trend: criminals aiming to steal corporate secrets and intellectual property with the intent to benefit in economic terms. The information leaked is usually resold to competing companies and governments interested in strategic know-how.
We must distinguish two scenarios:
- Cybercriminals steal information to perpetrate cyber fraud: spreading malware to steal a user's credentials for banking and payment platforms.
- Cybercriminals use technology to acquire sensible information to sell to highest bidder.
Uri Rivner, head of new technologies at RSA, is convinced that we are in the age of cyber espionage. Criminals steal trade secrets from other nations and companies for their own benefit. Consider another phenomenon: the impressive growth of internet availability in Asia Pacific, which has brought to this part of the world an increase of cybercrime and in particular of cyber espionage.
In this area, there is a growing demand for information technology that is often vulnerable to all sorts of cyber attack. These conditions make the market attractive to criminal organizations in the absence of effective regulations that often allow crimes to go unpunished.
The web is a jungle where it is increasingly difficult to defend our identity and resources. Rik Ferguson, director of security research and communication, Trend Micro declared:
"The reason why criminals are focusing their attacks on stealing personal data is simple. It's the sheer volume of people working from multiple devices that leaves them vulnerable to attacks,"
"While Trend Micro has been integral in working with authorities to break up a number of cybercriminal rings over the last year, these cybercriminals have acquired new techniques and tools from collaborating with one another to accelerate their 'industry.' The fact is: business is booming for cybercrime and everyone needs to take notice."
In the face of these ongoing threats, government agencies are defining best practices to reduce the risk of exposure to these attacks. NIST has recently made public their Draft Special Publication 800-83 (SP) Revision 1, Guide to Malware Incident Prevention and Handling for Desktops and Laptops. Malware is considered the most common external threat to personal computers, causing widespread damage and disruption and necessitating extensive recovery efforts within most organizations.
The publication provides recommendations for improving an organization's malware incident prevention measures, while giving extensive recommendations for enhancing an organization's existing incident response capability. These approaches seek to better handle malware incidents, particularly widespread ones.
Though cyber espionage as such is not considered one of the main activities of hacktivists, thoughtful security experts don't rule out the possibility. Groups such as Anonymous could easily adopt cyber espionage techniques to disclose sensitive information as a means of expressing dissent against a government or the policy of a private company.
When cyber espionage is deployed in the private sector (where companies spy on competitors, as well as their own employees, to capture vital information or to avoid unauthorized diffusion of confidential data), they acquire products from software outfits specializing in cyber espionage. The tools may be designed for justifiable purposes, such as supporting investigations and preventing of crime and terrorism. But too easily, they can be utilized by private businesses to undercut competitors, as well as by governments, in the bloodthirsty tracking and persecution of dissidents.
Social Media and cyber espionage
So far, this article has focused on cyber espionage based on the spread of malicious agents to gather confidential information. Also of great interest is cyber espionage as spread through social media. By accessing a social network profile, it is possible to acquire a lot of information on the victim; their relations; participation in events and discussions related to specific professional areas. The information gleaned could provide the basis for other types of attacks, as well as for a large cyber espionage campaign. By analyzing the relationships of a victim, it is possible to discover past experiences and use the data to create fake accounts, damaging their reputation and poisoning their professional network.
Starting with the assumption that the internet (and in particular, the social network) lacks a coherent and safe digital identity management, last year, I introduced the concept of social network poisoning: applying strategies designed to make knowledge related to a profile and its relationships unreliable. The application of this on a large scale could lead to the collapse of Social Networking, exposing members to the risks of cyber espionage and other cybercrime such as identity theft.
In the same way as "route poisoning," this "poisoning action," conducted with the aim of polluting the contents of social network profiles, typically introduces artifacts into existing real relationships, thus making the information unreliable. The result is the failure of the chain of trust which all social networks are based on, in order not to allow search engines specifically developed to retrieve information of any kind relating to a particular profile.
The principal espionage techniques implemented through social media platform are:
- Replacement of identity, or the ability to impersonate another user, using a wide variety of social engineering intelligence tactics.
- Simulation of identity, creating a false profile, which does not correspond to any existing person, for malicious purposes or simply to remain anonymous.
- Building of personal /social bots , creating a large number of fake profiles (e.g. millions of fake profiles) managed by machines, able to interact with real users in a way likely, thus changing the "sentiment" and "conversation" on a large-scale, as well as altering all the social graphs and precluding meaningful correlations on the data.
- black curation: the use of real (or fictitious) user's "holes" to speak on topics of which you want to change the meaning, or to create new ones ad-hoc, in analogy to the black SEO (search engine optimization) already use on search engines.
The social networks are excellent instruments to conduct cyber espionage campaigns while gathering information on targets. For this reason, it is strongly suggested that you consider carefully which profiles to add to our network, recognizing the possibility that some of them have been already compromised. This gives cyber criminals or spies the possibility of accessing information shared in the profile.
The intelligence industry in the west is still too vulnerable to all kinds of attacks, so it is absolutely necessary to define cyber strategies to deal with incidents like those described.
Last year, the impressive growth of state-sponsored attacks aimed at stealing information (to give economic, political and military advantages) famously included the cyber espionage campaign against NATO'S most senior commander, using the Facebook platform.

Chinese spies set up a fake Facebook account in the name of American Admiral James Stavridis, enticing his colleagues to "friend" him and thus divulge their own personal information. In the attack's second phase, Senior British military officers and Ministry of Defence officials accepted "friend requests" from the bogus account.
With this attack successfully completed, it became possible to steal sensitive information like private email accounts, photos and messages, as well as uncover his network of friends. Similar incidents are troubling, and show how even the higher echelons of strategic commands may be vulnerable, too.
If you think the information uncovered in this way is unimportant, you are mistaken. Let's think about how it can be used to find photos of a victim's residence, or determine his location at a given time. Further, with the knowledge of their private email account, it is possible to target people close to victims who may be misled by fake mails.
Of course, similar operations are hampered by the controls enacted by the managers of social networks, in collaboration with major institutions and law enforcement. The stakes are high and control of social networks is strategic. Many agencies and law enforcement agencies like the FBI are working to prevent such crimes. They've commissioned the development of complex analysis systems that monitor the powerful networks. Intelligence agencies are aware that social networks
and forums are exceptional instruments for information gathering and to measure the global sentiment on every kind of argument; political as well as social.
What is the future of cyber espionage?
The relentless spread of high-tech devices into our lives will sustain the practice of cyber espionage. Mobile and social networks are the platforms that attract the interest of attackers most of all, due to the large quantity of user's information they manage. New advanced toolkits are sold daily via the underground, usable to exploit vulnerabilities inside victim's machine with the primary purpose of installing malware that can gather confidential information.
From a government perspective, state-sponsored research aims to produce new technologies, able to infiltrate common-use objects. The most innovative ones relate to the use of electromagnetic waves that could spy on a targeted network or interfere with communications, altering the content of transmission (for example, introducing a malware
in it).
That is the future of cyber espionage: the possibility of interfering with targeted systems remotely, acquiring sensitive information silently. Another interesting field of research is related to the "intelligence of things": the possibility of exploiting the computational capabilities contained in every object surrounding us, interacting with users maintaining a huge quantity of information. Mobile devices, but really, any kind of appliance present in our home (such as smart-TV and gaming console) can be used to spy on the user. Governments have instituted an array of projects to exploit the vulnerabilities.
The greater the technological component of our lives, the greater the potential for cyber attacks.
References
http://www.uscc.gov/annual_report/2012/2012-Report-to-Congress.pdf
http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/drafts/800-83-rev1/draft_sp800-83-rev1.pdf
https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/flame-the-never-ending-story/

What should you learn next?
http://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Social_Network_Poisoning





